You are familiar with 404 errors because you have stumbled upon them countless times while searching for pages on Google or because they have made an appearance on your website at some point. No, they do not appear by magic; they always have a reason and must be corrected so that the site’s reputation with Google is not harmed.
Running into one of them is more common than it appears, and if you don’t pay attention to them, they can seriously harm the URL’s ranking and even the entire website.
We explain how they affect SEO and how to solve them using a real-world example from Interamplify.
What exactly is error 404?
Let’s review the concepts before we begin troubleshooting. The scenario is the same for all users: you click on a link, it automatically redirects you to a page, and a message appears informing you that the requested content is unavailable. You are facing the famous 404 “Not Found” error.
This is an HTTP status code returned to the user by the web server when the user attempts to access a URL that does not exist. In response, the server returns a page displaying the popular 404 page Not Found warning. That indicates the connection to the server was established, but the requested element could not be found. Isn’t it simple?
This is referred to as a broken link, and it can take the following form:
- 404 not found
- The requested URL was not found on this server
- HTTP 404 not found
- 404 ErrorPage cannot be found
404 Error – Causes
The most common cause of this type of error is that the web content has been removed or moved to another URL. However, there are additional reasons for this situation that you should be aware of:
- When a user manually enters a URL into the browser and makes a typing error.
- When a page is deleted intentionally or by mistake.
- When a URL is renamed and the old page is no longer available.
- When a domain is changed and the pages are not properly redirected. That is, the URLS of the old domain are not transferred to the new one.
- When the requested page does not exist.
- When the server or internet connection is unavailable.
404 Error – Consequences
As you may have guessed, this type of carelessness has negative consequences for a website’s organic ranking and should not be overlooked.
The most obvious consequence is the confusion that this type of broken links generate for the search engine crawlers, because they have the reason to interpret that the site is not being maintained correctly and conclude that it cannot meet the needs of the users.
As a result, the page’s ranking and number of visitors will suffer significantly. This has a direct impact on the site’s ranking and reputation.
As previously stated, Google’s goal is to provide a high-quality user experience so that users will continue to use its search engine. When crawling a page and repeatedly discovering that it lacks the content you seek, both the search engine spider and the end user lose confidence and leave the site quickly and without interacting. As noted previously, the trust you generate is critical for the EAT of your site in front of Google.
Another immediate consequence is the loss of quality external links to the domain authority and pointing to a removed page that was relevant.
It’s important to remember that Google only has a limited number of resources to analyze web pages in terms of ranking. This is known as the crawl budget, and it is proportional to how much Google trusts and respects your website. As a result, if you spend a limited amount of time crawling a page and analyzing errors, you will waste your budget on worthless URLs and make it more difficult to crawl pages that are worth ranking.
Finally, if it affects the user’s experience with the website, it directly alters the ranking, because if the user does not find what he or she expects, they will leave the page, return to the results, and click on another page of the SERPs.
This is a very powerful signal for Google known as Pogo Sticking, which informs the search engine that the result is not useful for the user and that the next result does satisfy the need.
As you can see, there is no such thing as an error without repercussions. But, thankfully, there are solutions for them as well. Continue reading to learn how we did it.
A real-life example of implementation in Uruguay
We received a letter a few weeks ago from an American client who had decided to internationalize his project. He stated that he intended to begin in Latin America, specifically in Uruguay. To that end, he created country subdomains a few months ago with the aim of supporting geolocation in Google.
Later on, he decided to give it autonomy and create a separate domain for each country. However, something was going on with the original US page, as it began to lose positions in the results pages for URLs that were already well ranked.
He was also unable to stand out with the Uruguayan domain, so he requested our assistance in determining what was preventing him from growing.
You’re correct if you guessed the problem. Some URLs from the old subdomain had been removed arbitrarily and were littered with 404 errors, while others remained and competed for the same keywords as the URLs on the new domain.
When a website grows in size, its structure becomes more complex, and it is likely that many pages containing 404 errors are created without the owner’s knowledge. For this reason, the first thing we did for our client was conduct a technical audit. This assisted us in detecting the broken links on their website.
You’ll need the right tool for this. In our case, we use Google Analytics, and as we show you in this case study you can detect them quickly in just 3 steps:
- Access the “Behavior” menu and select “all pages”.
- Set “Page Title” to primary dimension.
- Finally, type in the search engine “404”.
The tool will display a list of errors similar to the ones our client experienced, as shown below:
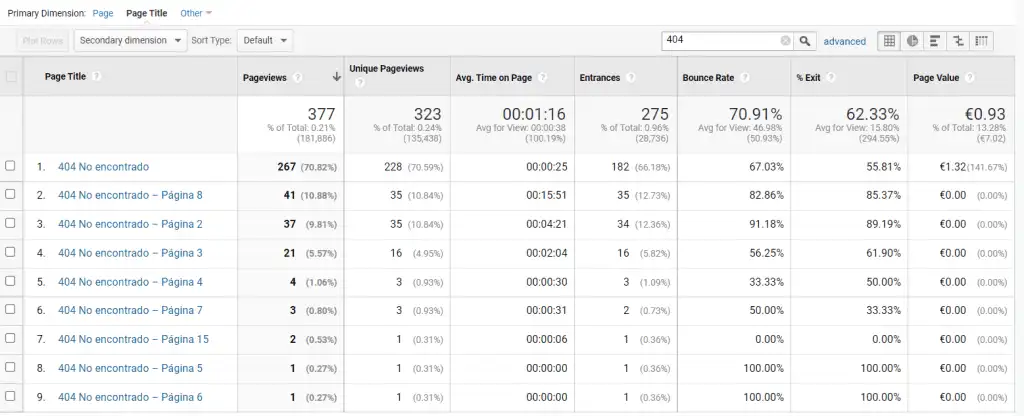
Of course, Google has taken notice, and its response is obvious. It has penalized the page and relegated it to low-visibility SERPs.
We extracted all of the errors and transferred them to a spreadsheet, where we evaluated each option one by one. The solutions we considered are listed below.
Do you require our assistance in detecting 404 errors on your website?
If you make a mistake and don’t fix it…
You will be making a major mistake. A 404 error is not negative when it is justified, but solutions must be found to avoid a bad user experience. It is common practice to modify internal links pointing to 404 pages in order to assist users in finding what they are looking for. We did it this way at Interamplify:
1.Redirecting
301 redirects to another page, which is also known as RedirectMatch 310. It enables you to redirect the user to the desired content, but on a different URL than the one he previously visited. When the user finds the error link, he will be redirected to an equivalent page with content as similar as possible.
We have used redirect 301 when the client´s URL:
- It has good authority.
- It registers high-quality traffic.
- It has a good ranking.
- All of the preceding points are related.
- If it is a large number of links that does not allow to go one by one or takes a long time.
410 Error: indicates that a specific URL no longer exists and that Google should no longer crawl it.
We have used error 410 when the client URL:
- Contains no internal links, lacks traffic and authority.
- It was created on the go and is no longer associated with any of the current URLs.
- Cannibalization occurs between two URLs.
If you look closely, you will notice that we used error 410 for URLs that do not provide SEO value to tell Google not to waste time crawling non-existent URLs and to focus its efforts on those that do, for which we used the 301 redirect.
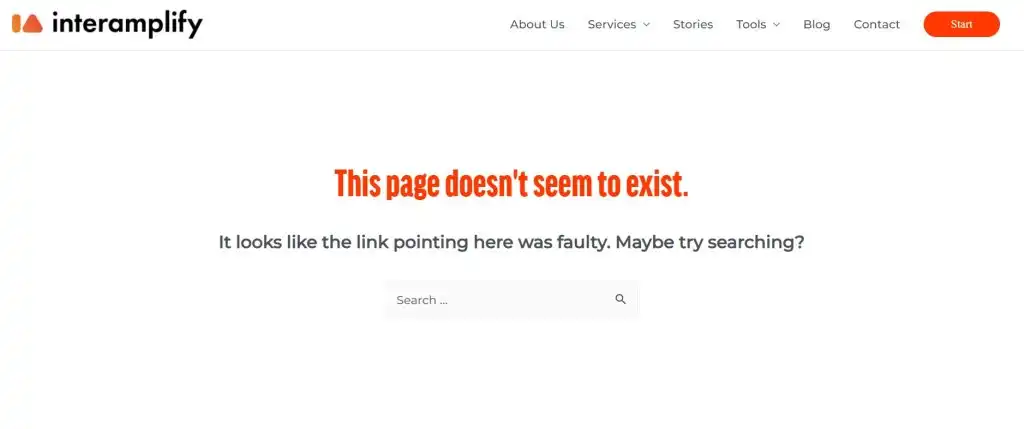
2.Make your own, personalized 404 error page
We proposed to the client the creation of a personalized page that retains their attention and prevents them from abandoning the visit when they encounter an unavoidable 404 error on the site in order to prevent them from returning to the search results. This is indicated in cases where this type of error is unavoidable, with the goal of showing the user alternative paths to take. There are some benefits to replacing the standard Google “Not Found” page:
- Create a site that conveys peace of mind.
- As a result, it improves the website’s user experience and engagement.
- It is an effective way to reduce user frustration and avoid high bounce rates.
Generic 404 error pages don’t tell the user what to do next, but this can be fixed with a personalized page. Here are some of the alternatives we offer our clients:
A button that returns you to the home page, or the addition of a search engine, as we do in Interamplify:
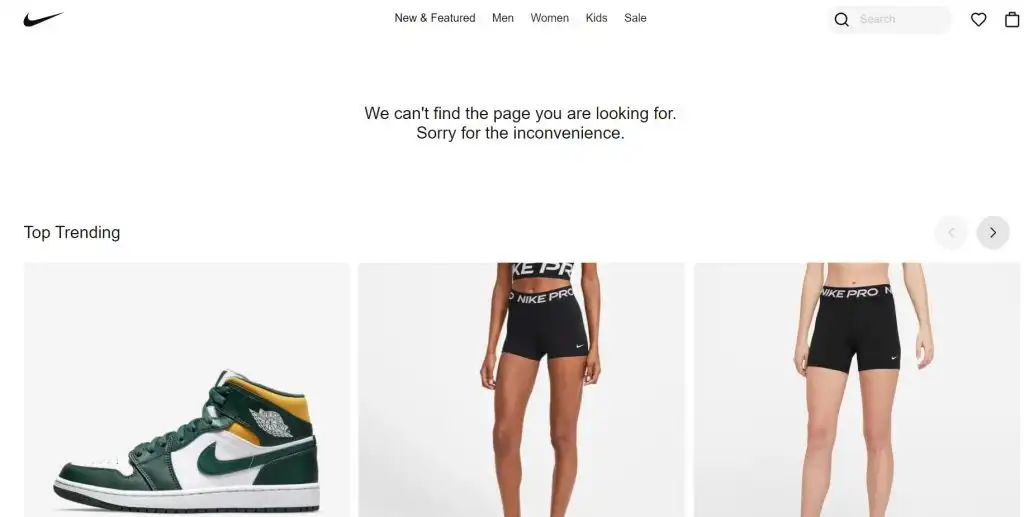
You can use the opportunity to encourage cross-selling and highlight some of your best-selling products, as Nike does on its website:
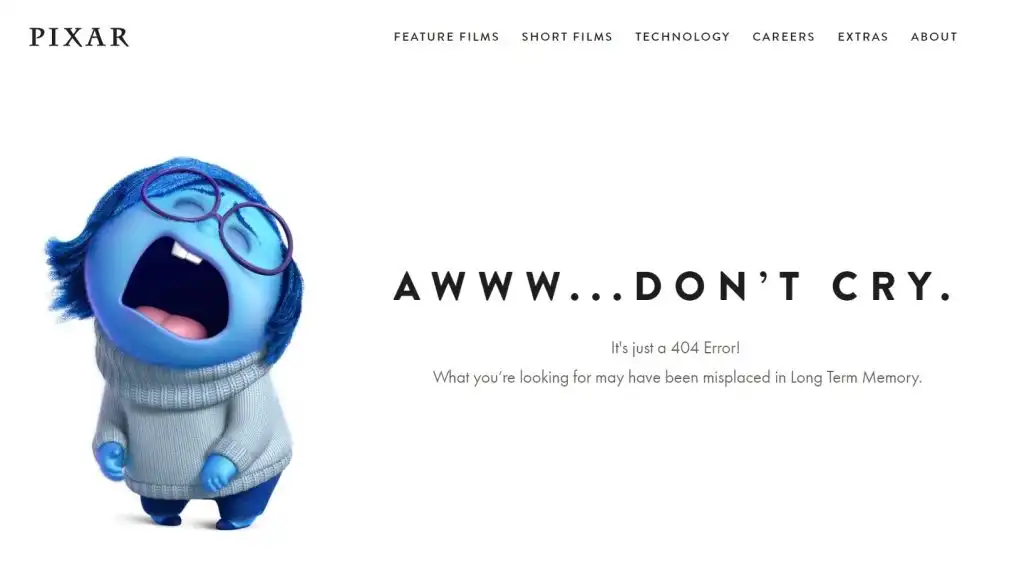
Another option is to seek positive impact through originality in order to increase customer loyalty. Consider the following Pixar example:
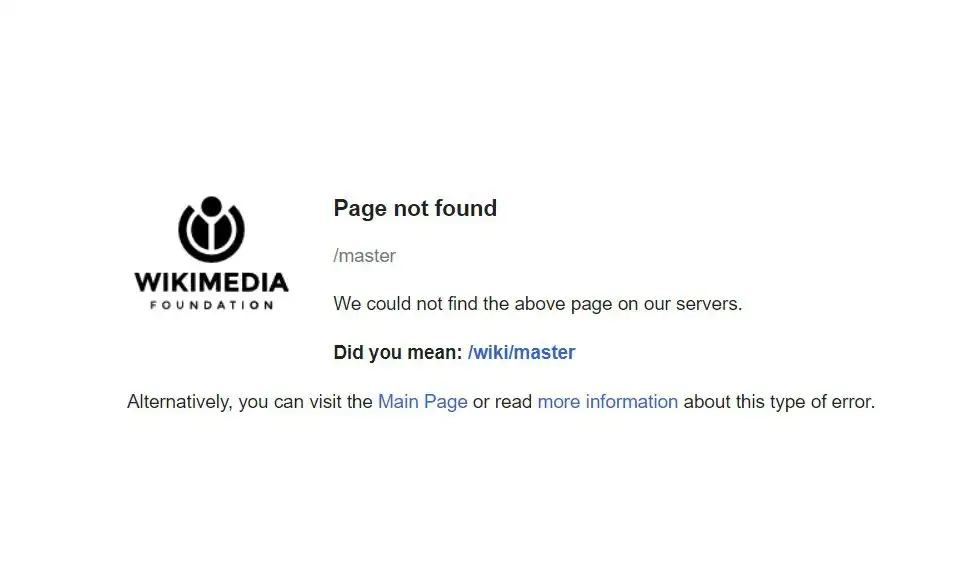
You can also offer valuable content, a download, or any other resource that will convert a lost user into a web surfer. Wikipedia takes advantage of the opportunity to provide several solutions, including links to the 404 error file, an alternative search, and the home page.
There are numerous options, so we recommend determining what content you have available to attract the attention of your buyer persona.
What matters most to us…
Before we part ways, keep one thing in mind: don’t fall victim to the 404 error. When this type of situation is unavoidable, offer your visitors an alternative, as it may become an opportunity to convert a lost user into a loyal customer.